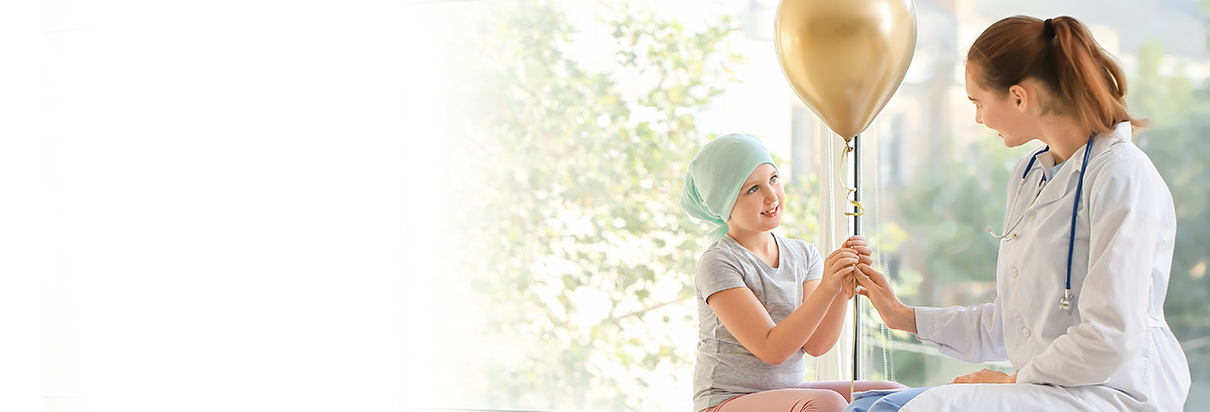Answering the unmet nutritional needs
Disease-related malnutrition may lead to an alteration of growth and development in children, as a consequence.1 It can be exceptionally challenging to meet the nutritional requirements of acutely or chronically ill children.2 Parents may need your supervision to meet their kids’ nutritional requirements.
Frebini® Drinks are specially formulated to help you support your little patients with complete nutrition they really like. Knowing that EN products are only helpful when consumed entirely, Frebini® Drinks’ great taste is approved by kids, so that they may help improve the quality of life for the whole family.
The goal of nutritional support for the paediatric patient is to provide adequate amount of energy and nutrients to fill up the energy gap.5
Oral Nutritional Supplements (ONS) are used to increase the total daily protein, calorie, and micronutrient intake in order to improve weight gain and nutritional status.5
ONS have been shown to improve catch up growth in undernourished children as well as promote growth with long term usage.
Oral Nutritional Supplements (ONS):6- 8
 May help to increase energy intake in a variety of diseases in children
May help to increase energy intake in a variety of diseases in children
 May help to improve body weight and growth in children with a variety of diseases
May help to improve body weight and growth in children with a variety of diseases
 May provide clinical benefits by improving the nutritional status of the child
May provide clinical benefits by improving the nutritional status of the child
ONS are an easy and effective way to tackle malnutrition!
Dedicated to support a healthy growth
Frebini® ENERGY (FIBRE) Drink supports kids on their journey to Grow & Thrive (GT) with high energy, high-quality protein, an adapted fat profile, tailored micronutrients and special ingredients.
Specifically developed, according to the latest recommendations, Frebini® ENERGY (FIBRE) Drink is based on state-of-the-art scientific evidence and Fresenius Kabi’s long-term experience in Enteral Nutrition, offering comprehensive support for the dietary needs of kids with or at risk of malnutrition.
Frebini® ENERGY (FIBRE) Drink is a commitment to your little patients’ wellbeing. The tasty flavour alternatives support higher nutritional needs without giving up on taste, making mealtimes more pleasant for kids.
Frebini® ENERGY (FIBRE) Drink*
supports kids to Grow & Thrive (GT) with all four essentials
High Energy
300 kcal (1260 kJ) of energy
Adapted Fat Profile
8% energy from MCT**, which are fast and efficient energy supplies, for easy digestion, absorption and good tolerance
High Quality Protein
7,6 g of high quality milk protein, ensuring maintenance of muscles
Micronutrients & Special Ingredients***
Vitamins e.g. 3,0 µg of vitamin D;
Minerals e.g. 210 mg of Calcium;
Trace elements e.g. 2,4 mg of Zinc and
Special ingredients e.g. 9,0 mg of Carnitine, 24, 8 mg of Taurine, 45 mg of Inositol



Nutritiously delicious
Taste is a priority for all children, and the success of nutritional support depends on their acceptance and liking. That’s why we asked the kids to evaluate Frebini® Drinks in an independent taste study.
The results showed that the children well accepted the taste alternatives of Frebini® Drinks.
Recipes with Frebini® ENERGY (FIBRE) Drink
Frebini® ENERGY (FIBRE) Drink blends nutrition with a great taste that kids enjoy.
Our recipe booklet offers a treasure of imaginative ways to integrate this drink into meals. Curious to see what’s inside? Explore the recipes and let your kids discover the great taste.
Download Recipe Booklet
Let your patients enjoy the great taste with yummy recipes
Frebini_ENERGY_(FIBRE)_DrinkRecipe-Booklet.pdf
Let your patients enjoy the great taste with yummy recipes
- Filename
- Frebini_ENERGY_(FIBRE)_DrinkRecipe-Booklet.pdf
- Size
- 7 MB
- Format

The 200 ml child-friendly EasyBottle is easy to hold, practical to carry on and ready for support when or wherever your child needs.
Explore the products page to learn more about Frebini® Drinks:

*Versions with fibre to maintain gut health, and fibre-free for patients who cannot tolerate fibre
**With high quality complete milk protein (80% casein, 20% whey) for a balanced amino acid provision and catch up growth and/or disease specific higher demands.
***Medium Chain Triglycerides
****According to legal requirements
*****Excluding Vanilla flavour
References:
1. Mehta NM, Skillman HE, Irving SY, Coss-Bu JA, Vermilyea S, Farrington EA, et al. Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Pediatric Critically Ill Patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017;18(7):675-715.
2. UNICEF. Challenges in the management of malnutrition in children. https://www.unicef-irc.org/article/959-challenges-in-the-management-of-malnutritionin-children.html
3. Mehta NM, Corkins MR, Lyman B, Malone A, Goday PS, Carney LN, Monczka JL, Plogsted SW, Schwenk WF; American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Board of Directors. Defining pediatric malnutrition: a paradigm shift toward etiology-related definitions. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2013 Jul;37(4):460-81. doi: 10.1177/0148607113479972. Epub 2013 Mar 25. PMID: 23528324.
4. Dipasquale V, Cucinotta U, Romano C. Acute Malnutrition in Children: Pathophysiology, Clinical Effects and Treatment. Nutrients. 2020 Aug 12;12(8):2413. doi: 10.3390/nu12082413. PMID: 32806622; PMCID: PMC7469063.
5. Cederholm T, Barazzoni R, Austin P, Ballmer P, Biolo G, Bischoff SC, Compher C, Correia I, Higashiguchi T, Holst M, Jensen GL, Malone A, Muscaritoli M, Nyulasi I, Pirlich M, Rothenberg E, Schindler K, Schneider SM, de van der Schueren MA, Sieber C, Valentini L, Yu JC, Van Gossum A, Singer P. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition. Clin Nutr. 2017 Feb;36(1):49-64. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 14. PMID: 27642056.
6. Francis DK, Smith J, Saljuqi T, Watling RM. Oral protein calorie supplementation for children with chronic disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 May 27;2015(5):CD001914. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001914.pub2. PMID: 26014160; PMCID: PMC4460719.
7. Huynh DT, Estorninos E, Capeding RZ, Oliver JS, Low YL, Rosales FJ. Longitudinal growth and health outcomes in nutritionally at-risk children who received long-term nutritional intervention. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2015 Dec;28(6):623-35. doi: 10.1111/jhn.12306. Epub 2015 Mar 25. PMID: 25808062; PMCID: PMC6680231. 8. T, Hoang TN, Ngo NT, Nguyen LH, Tran TQ, Pham HM, et al. Effect of Oral Nutritional Supplementation on Growth in Vietnamese Children with Stunting. The Open Nutrition Journal. 2019;13(1):43-52.
9. UNICEF. Ready-to-use therapeutic food for children with severe acute malnutrition. 2013. https://www.unicef-irc.org/files/documents/d-3838-Position-Paper--Ready-to-.pdf