Combines the benefits of two procedures
The technique combines the advantages of a conventional PEG placement using the pull method with the benefits of a secure adaptation of gastric wall and abdominal wall, independent of PEG fixation.
In 1980, Ponsky and Gauderer developed a new endoscopic method for percutaneous feeding tube placement. The so-called PEG was born. This innovation was groundbreaking as it allowed long-term feeding tube placement with only minimal intervention.
Fresenius Kabi launched its first Freka PEG soon after in 1984 and has continuously improved it since then. It has now become the gold standard for gastroenterologists to place an enteral feeding tube. Due to its long durability, Freka PEG is particularly suitable for long-term nutrition. It does not need to be replaced frequently and can last for years with good aftercare1. The Freka PEG Pro range with the same tube design and more safety features a further step in product improvement.
The Freka PEG Pro can be extended with the compatible Freka Intestinal tube for jejunal nutrition. And various balloon feeding tubes are available to replace the Freka PEG Pro in a mature stoma canal. These include the Freka Belly Button range and the Freka Belly GastroTube range.
The body gets the energy it needs
The patient can be flexible and mobile while eating
Do not worry about enough eating
No more pressure to eat orally
More quality time for the patient
It is really a discreet solution

The technique combines the advantages of a conventional PEG placement using the pull method with the benefits of a secure adaptation of gastric wall and abdominal wall, independent of PEG fixation.
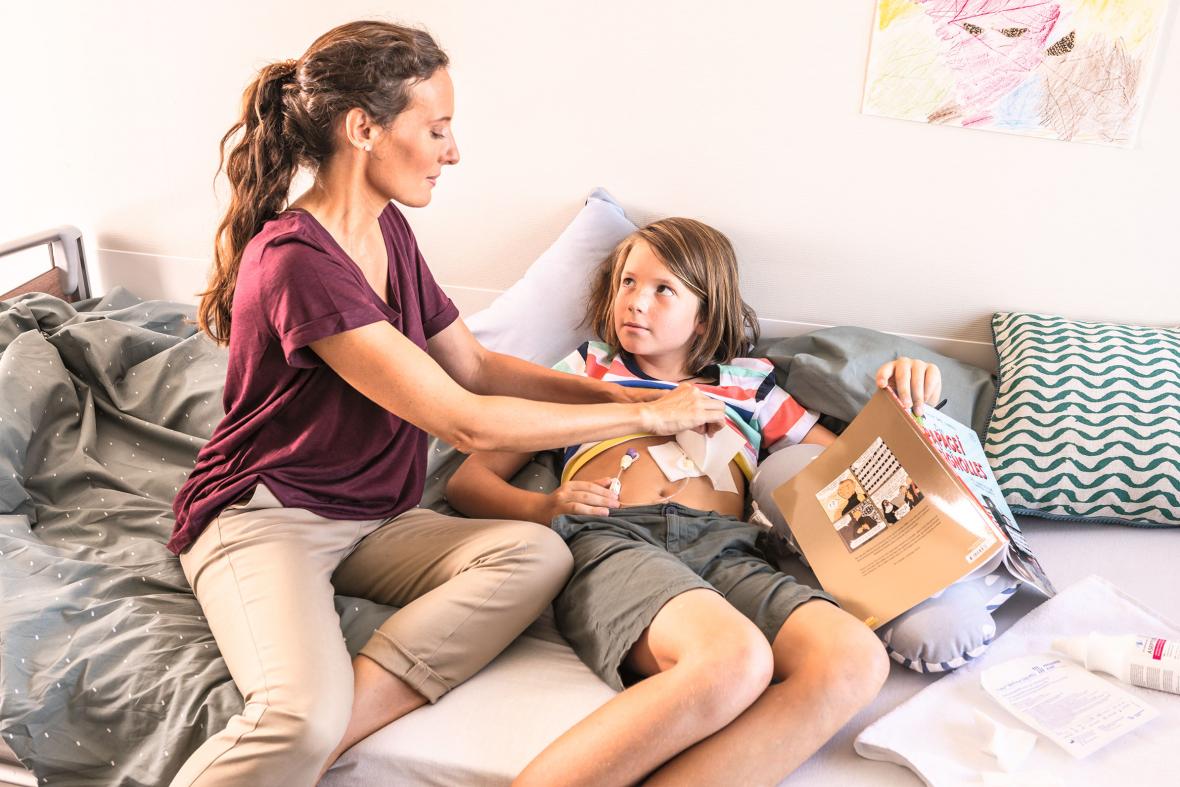
Gastropexy lowers PEG complications by up to 85% (2,3), safeguarding the stoma and preventing peritoneal gastric juice infiltration, thus reducing infection risks.
Unlike traditional PEG, after gastropexy, the outer PEG plate can be loosely fixed against the abdominal wall2. Thus, a better blood circulation around the stoma enhances stoma healing and early tube mobilization prevents from buried bumper syndrome4.
This procedure offers enhanced protection for PEG patients, especially those with compromised health conditions like cachexia, wound healing issues, and diabetes, yielding significant benefits.
The data ... show ... that the direct
puncture procedure lead to a significant
reduction in complications, especially
major complications, ...
(Kishta J, Reich V, Bojarski C. Hybrid-PEG – Erfahrungen nach über 300 Hybrid-PEGs an der Charité. Endo-Praxis 2021; 37: 95–99 – article in German)

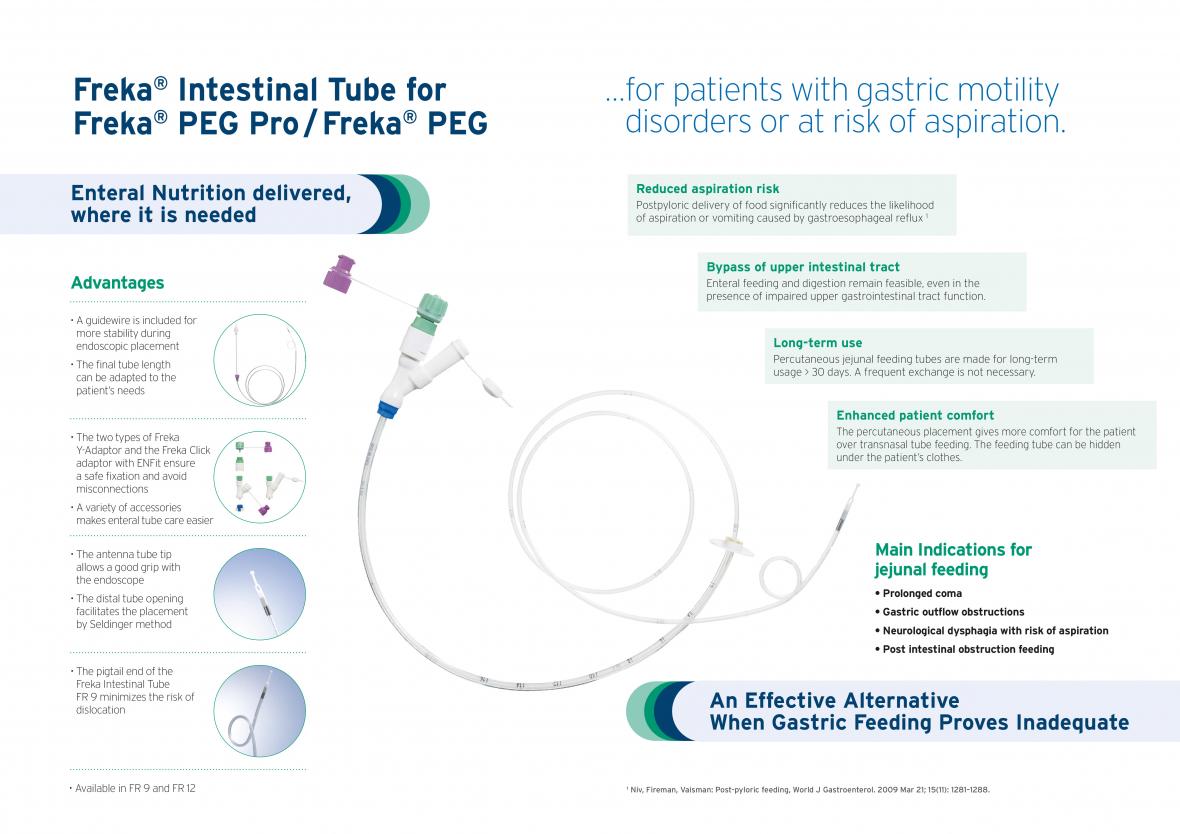
Administering nutrition via a jejunal feeding tube involves delivering nutrients directly into the small intestine, bypassing the stomach. This approach reduces the risk of aspiration pneumonia, a critical consideration for individuals with compromised swallowing reflexes or other medical conditions predisposing them to aspirate stomach contents.
The Freka Intestinal Tube is a jejunal extension tube for the gastic Freka PEG Pro. The Freka PEG Pro serves as a guiding tube for the Freka Intestinal tube allowing intestinal acces as well as gastric access.
1 Sartori, S., et al., Longevity of silicone and polyurethane catheters in long-term enteral feeding via percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2003. 17(6): p. 853-6
2 Kishta J, Reich V, Bojarski C. Hybrid-PEG – Erfahrungen nach über 300 Hybrid-PEGs an der Charité. Endo-Praxis 2021; 37: 95–99
3 Leonie Schumacher, Christian Bojarski et. al, Complication rates of direct puncture and pull-through techniques for percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy -Results from a large multicenter cohort, DOI: 10.1055/a-1924-3525, 08/2022
4 Devia J, Santivañez JJ, Rodríguez M, Rojas S, Cadena M, Vergara A. Early Recognition and Diagnosis of Buried Bumper Syndrome: A Report of Three Cases. Surg J (N Y). 2019 Aug 22;5(3):e76-e81. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1692148. PMID: 31448333; PMCID: PMC6706275.