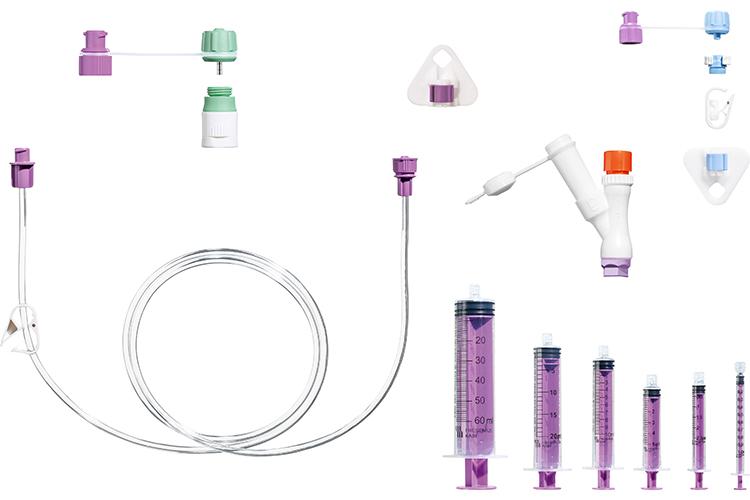
Freka - the percutaneous feeding tube range by Fresenius Kabi
To meet the needs of the healthcare professionals and their patients
Sophisticated design developed in collaboration with users and healthcare professionals
Nutrition can sometimes be difficult for a variety of reasons, e.g. in case of neurological swallowing disorders or passage disorders in oncological patients. Also, children or adults with disabilities may not be able to get sufficient food intake.
Such underlying conditions can give rise to the early assumption that enteral nutrition will be necessary for these patients over a longer period. If the nutritional support is foreseen to exceed 4 weeks, placement of a percutaneous feeding tube should be considered.
To meet the needs of the healthcare professionals and their patients
Sophisticated design developed in collaboration with users and healthcare professionals

Placement:
A percutaneous feeding tube is placed through the abdominal wall
directly into the stomach:
Endoscopically - Laparoscopically - Surgically
Why percutaneous?
A long-established team of experts from Fresenius Kabi have been constantly developing and improving the tube range for almost 40 years. Percutaneous tubes can be classified into initial placement tubes and replacement tubes. Initial placement tubes must ensure safe fixation of the stomach wall to the abdominal wall until a stoma is formed. They can be placed either endoscopically, laparoscopically or surgically. Replacement feeding tubes have usually a balloon as the inner retention device, which can be inflated or deflated for easy exchange in a mature stoma tract.
Over the years a Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) has become standard for initial placement of a percutaneous feeding tube.
The Freka PEG Pro from Fresenius Kabi is made of polyurethane, a proven and soft material. Well-engineered details make the use of the Freka PEG Pro reliable and comfortable for both, the healthcare professional and the patient.
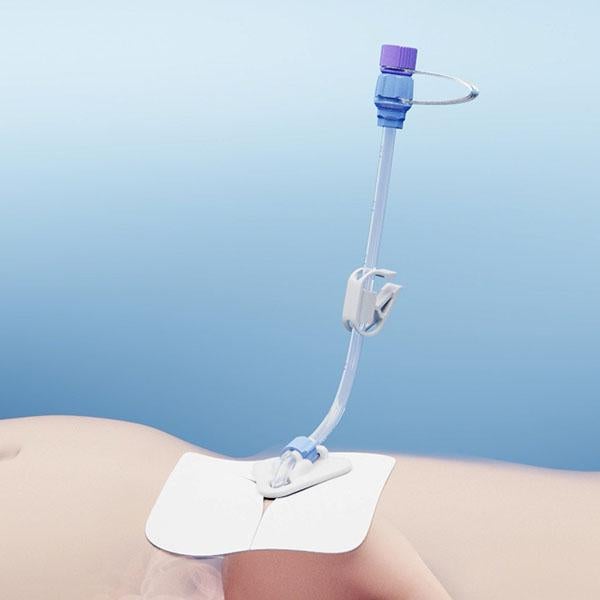
In case of gastric outlet obstructions, jejunal feeding might be required. The Freka Intestinal Feeding Tube can be inserted through a Freka PEG. The PEG serves as a guiding tube.
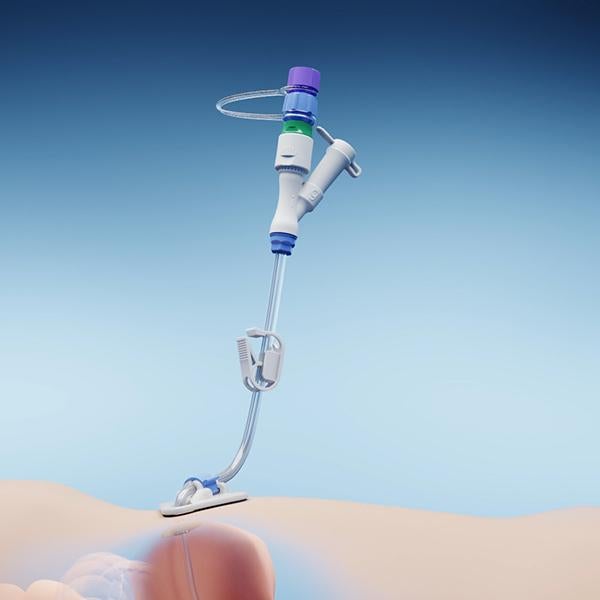
The Freka PEG Pro Hybrid Set is a procedure pack with a Freka PEG Pro and a Gastropexy Device. A gastropexy performed prior to a PEG placement ensures a safe fixation of the gastric wall to the abdominal wall. This enables a better wound healing.
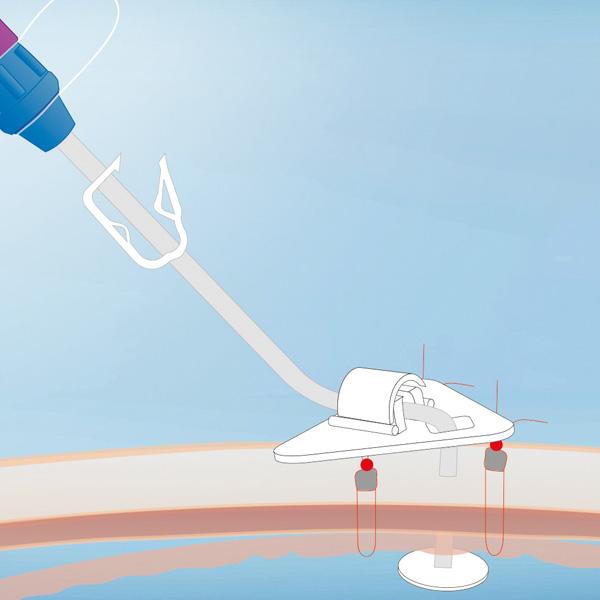
As an alternative to a PEG, a similar feeding tube can be placed by using the direct puncture method. For this, the stomach wall is sutured to the abdominal wall by gastropexy before puncturing the stomach. A Balloon feeding tube can be placed initially. Fresenius Kabi offers a sophisticated kit with a special gastropexy device.
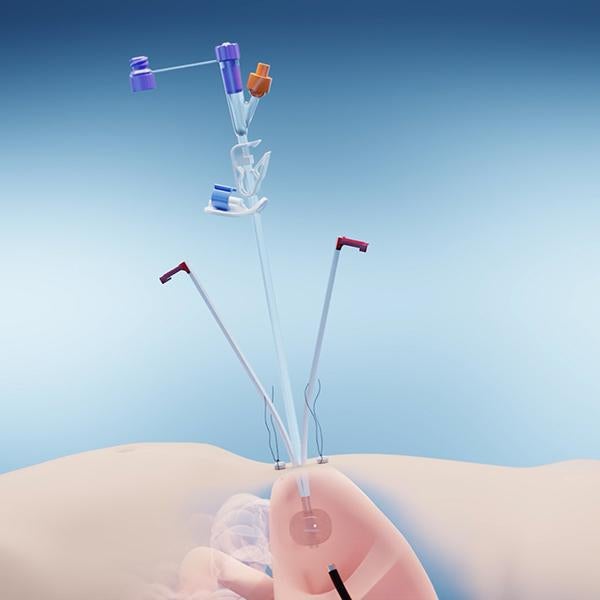
The Freka FCJ (Fine Needle Catheter Jejunostomy) is a jejunal feeding tube, that can be placed at the end of a major abdominal surgery or by laparoscopy. The Freka FCJ supports early post-operative feeding for a longer period.
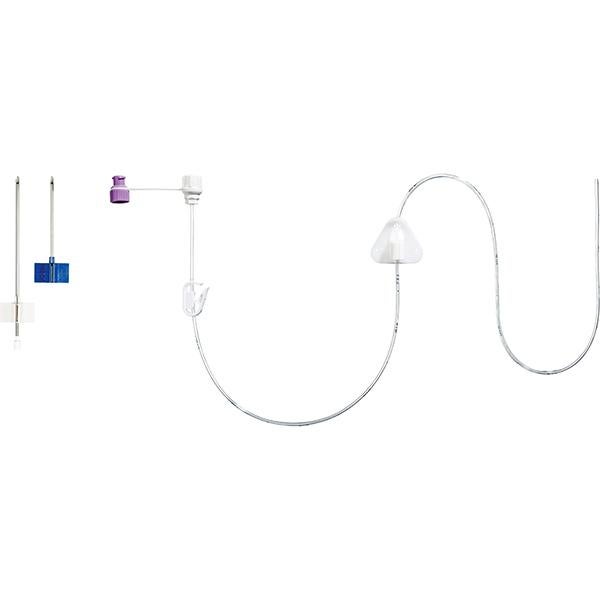
Freka Belly Button can be used in a mature stoma tract. An inflatable balloon serves as the inner retention. The shaft length corresponds to the individual stoma tract length. A special stoma measuring device is available for determining the stoma tract length.
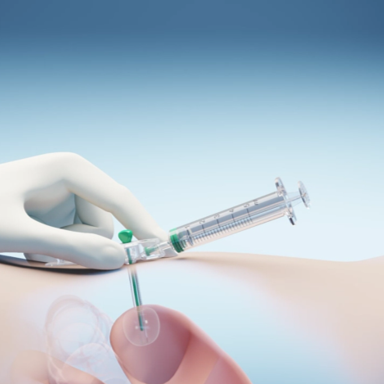
The Freka Belly GastroTube is a replacement feeding tube with an inflatable balloon as the inner retention. It is made of soft silicone rubber.